How to Treat Mouse Elbow
Mouse Elbow… it’s a Thing
So what exactly is mouse elbow? Also known as lateral epicondylitis, it refers to inflammation in the extensor tendons of your forearm. It may also include inflammation in the extensor muscles that allow your hand to open and your wrist to bend [1, 2]. People who constantly use a computer mouse, like avid gamers or eSports professionals, are more susceptible to this type of injury.
The Anatomy of a Mouse… Elbow
To get a better understanding of how this condition develops, it’s important to learn about the anatomical structure of the forearm, hand and wrist. The tendons affected by mouse elbow are collectively known as the common extensor tendon. It consists of four muscles and tendons that join in one area called the lateral epicondyle. Additional structures that may be involved include:
- The extensor digitorum
- The extensor digiti minimi
- The extensor carpi ulnaris
- The extensor carpi radialis brevis
- The extensor carpi radialis longus
- The supracondylar ridge
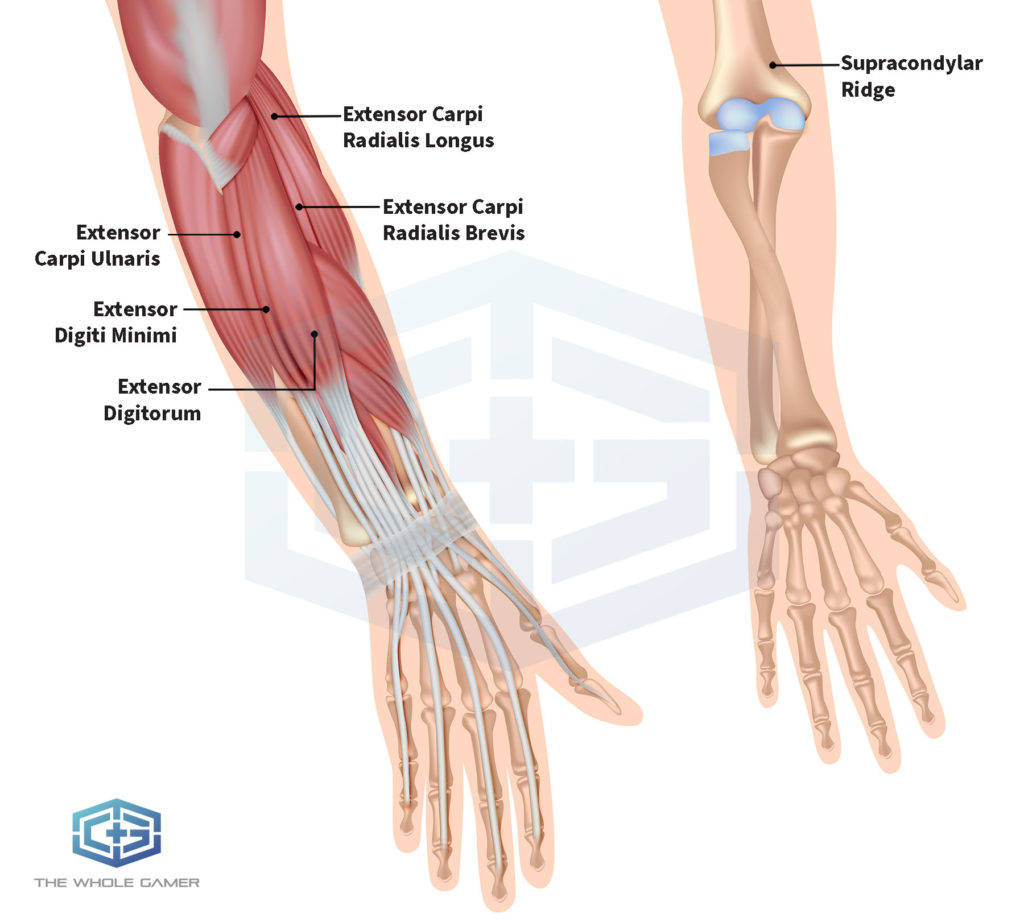
These structures enable fine motor movements of the fingers, hands, wrist and forearm. The tendons and muscles also extend into the elbow region. Gaming and eSports enthusiasts develop mouse elbow after repeatedly holding and pressing mouse buttons while moving their arm. This causes the extensor tendons and muscles to constrict and contract repeatedly, leading to pain in the common extensor tendon (the outer region of the elbow) that may extend toward the forearm, wrist and hand [2]. This occurs because over time, repetitive gaming motions weaken and tire the extensor muscles and tendons in the forearm. These motions include gripping, squeezing and shifting a mouse, as well as pressing controller buttons or using a scroll wheel. If mouse elbow is left untreated, it can lead to the degeneration of collagen, a structural protein that supports connective tissue in the common extensor tendon [1-3].
The Symptoms
Symptoms of mouse elbow include…
- Pain in the outer elbow area
- Pain in your wrist when gripping or squeezing the mouse
- Pain bending your fingers or wrist backward (this contracts extensor muscles)
- Pain while flexing your fingers and wrist forward (this stretches extensor muscles)
- A weakened grip due to constant pain while gaming
Prevention Methods and Treatment
Here are a few strategies that can help treat mouse elbow and prevent it from worsening.
- Rest the affected arm so it has time to heal
- Gradually try strengthening and mobilizing exercises to improve circulation and muscle tone [4]
- Work with a specialist to make sure you’re performing these exercises properly [5]
- If you think you have mouse elbow, seek treatment right away, before it gets worse
Addressing mouse elbow early is the key to getting back into the game!
References
- Kahlenberg CA, et al. New Developments in the Use of Biologics and Other Modalities in the Management of Lateral Epicondylitis. Biomed Res Int. 2015; 2015: 439309.
- Andres BM, et al. Treatment of Tendinopathy: What Works, What Does Not, and What is on the Horizon. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2008;466(7):1539-1554.
- Calfee RP, Patel A, DaSilva MF, Akelman E. Management of lateral epicondylitis: current concepts. Journal of the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons. 2008;16(1):19-29.
- Croisier JL, Foidart-Dessalle M, Tinant F, Crielaard JM, Forthomme B. An isokinetic eccentric programme for the management of chronic lateral epicondylar tendinopathy. Br J Sports Med. 2007;41:269-275.
- Smidt N, van der Windt DA, Assendelft WJ, Deville WL, Korthals-de Bos IB, Bouter LM. Corticosteroid injections, physiotherapy, or a wait-and-see policy for lateral epicondylitis: a randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2002;359:657-662.














